Our Advantages
Our new saliva-based RDT for malaria detection is based on
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) detection mechanism. We
are going to detect P.falciparum lactate dehydrogenase, which is a
biomarker for the presence of Malaria parasite, level in saliva. With
this technology, our device will be able to fully quantify the level
of infection; thus, the patients will only need to take appropriate
amount of drugs. .
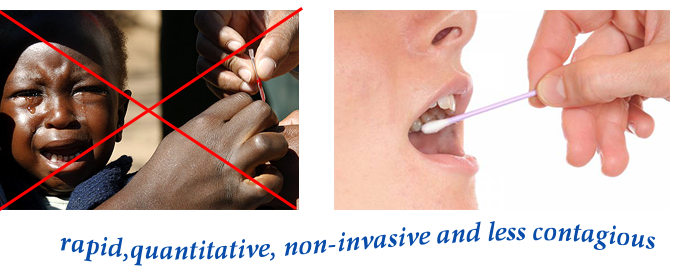

This is a great advantage of our device,
since most Malaria RDT on current market can only offer
qualitative readout, so the patients will have to take a maximum
dose of drug treatment. This will potential lead to antimalarial
drug resistance issue. More importantly, our approach to detect
malaria parasite is based on saliva, which is non-invasive and
less contagious comparing to the use of blood from most current
RDT approach. We believe that saliva sample collection will be
more favored by patients than finger-prick blood collection,
especially when the patients are children or babies.
